Disruptive Technologies: Forging the Future of Computing and Data Centers
The world is and always has been shaped by innovation. While many significant technologies have been built incrementally over years or even decades, every now and then an “aha” moment presents a profound and disruptive breakthrough, changing the course of history.
What is Disruptive Technology?
Disruptive technology refers to an innovation that transforms an established technology, process or product to significantly change the way a business, industry or consumer operates. Unlike sustaining innovations, which seek to improve existing products, disruptive technologies replace established solutions by opening new business models and revenue streams to serve untapped markets – often rendering existing solutions obsolete.
While these technologies may seem to come out of nowhere, they are not necessarily new or cutting-edge: They generally have been established for some time before turning a market or industry on its head. What makes it disruptive is how that technology is applied in a new way. It’s not just an advancement. It’s a paradigm shift.
A Technology Paradigm Shift
Think about the history of streaming services. Netflix, for example. Video rental services and cable broadcasting were established well before the advent of streaming. To get into the market, Netflix adopted mailing as a service to provide DVD rentals to customers. The innovation – mail – was hardly anything new. What mattered was how it was applied to build an entirely different business model.
But even Netflix displaced its own way of doing business when video streaming came into play. Early technology to download videos as an add-on service was limited to personal computers. Remember the days of Macromedia and Adobe Flash? The technology was there, but it was mainly used for short video snippets. Once YouTube launched internet video into the mass media, Netflix quickly caught on – propelling the video broadcasting industry and giving rise to the streaming giants we see today.
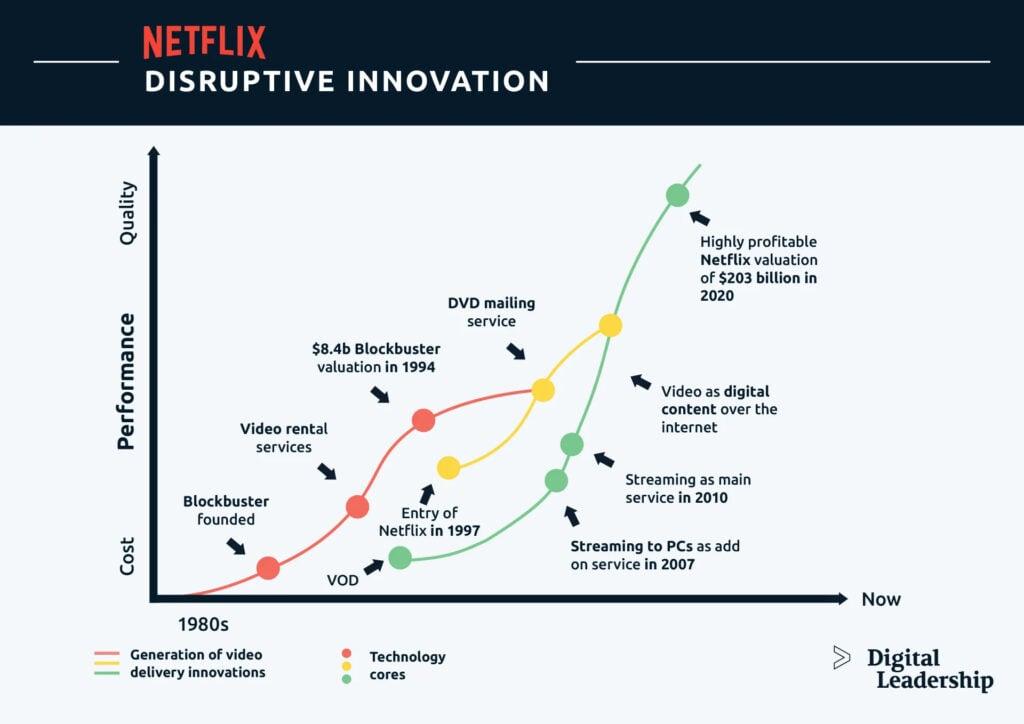
Now, streaming seems to be built into everything. We can catch up on the latest episode of our favorite show, talk to our mom on Facetime, join a quick video conference and even take virtual tours of a home on the market. The possibilities are endless. And the next disruptive technology to come to this industry may already be in the works.
Disruptive Technology in the Computing Industry
For decades, the computing industry has been a hotbed of disruptive technology – constantly reshaping the way we live and work. From personal computers to the internet to the rise of cloud computing, the impact of these innovations has been deep and continue to redefine the industry.
Artificial Intelligence
Perhaps the most widely known and high-profile disruptive technology is artificial intelligence (AI). This enables machines to perform cognitive functions similar to the human mind such as perceiving, reasoning and problem-solving. Think virtual assistants, fraud detection, healthcare treatment recommendations, facial recognition, self-driving car navigation…heck, even the streaming giants use AI to suggest movies based on your preferences.
AI’s ability to process large amounts of data to form predictions (and adapt, based on new information) makes it a versatile tool for any business process. And the benefits are widespread, bringing increased efficiencies, improved customer service and scalability to organizations. In fact, AI adoption has more than doubled since 2017, with roughly 50% of businesses deploying at least one AI capability in their business processes today.2
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an emerging technique within the AI spectrum that focuses on understanding spoken language as well as text. It uses computational linguistics to recognize, parse, interpret, translate and generate speech from unstructured data.
Ever heard of ChatGPT? How about Apple’s Siri or Amazon Alexa? All these use NLP to interpret human language to perform a specific task. It’s quite complex, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg. The ability to summarize, translate and index large texts will bring a wealth of information to the forefront.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) integrates information from text, graphics, audio and other virtual sources with real-world objects. Unlike virtual reality, which is completely virtual, AR enables users to control their presence in the real world.
Essentially, AR takes in your surroundings and provides a visual overlay on top of it, so the user can move freely throughout the world while receiving additional information and images. AR has been used in construction to visualize mechanical, electrical and plumbing systems within a building, aided in equipment repair, and even in medical training.
AR provides enhanced data visualization and analytics – leading to a plethora of advantages for businesses. Encouraging interactions, improving workflows, optimizing training, streamlining product design, reducing risks…there’s immense potential. It’s no surprise that the market for augmented reality is expected to grow nearly 40% in the next seven years.3
Blockchain
Blockchain radically changed the way businesses manage data and conduct transactions. Essentially, it is a shared database that provides a highly secure, permanent record of all digital events between participants. Blockchain stores data in a series of blocks, each holding a set of information that is validated, secured and immutable. When a new transaction occurs, a new block is added, and the entire chain is updated.
Blockchain technology use cases far exceed cryptocurrency. Healthcare providers use it for confidentiality and compliance in exchanges with patients and their records. Financial services benefit from secure transactions and trading. Supply chains utilize blockchain for traceability, verification and counterfeit prevention.
Blockchain is becoming so popular that nearly 90% of businesses have reported deploying some type of blockchain technology, and 87% plan to invest more in the next year..4
Cryptography
Cryptography is a security practice that keeps information safe through the use of codes that can be deciphered only by authorized parties. The simplest method is data encryption which scrambles text and then rearranges it so it’s readable only to the intended recipient.
Businesses concerned about cybersecurity use cryptography to encode and decode data to secure communication, prevent theft or interception for transactions, protect data privacy and enhance online security.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems at unbelievable speeds – up to a million times faster than a personal computer. Because it’s able to process many sequences simultaneously, deeply intricate statistical problems can be solved almost instantly.
Think of quantum computing like climbing a mountain. Traditional computing methods follow one path to the top without considering the other possible pathways. Quantum computing provides a map view in which all routes are explored at the same time. That gives huge potential to businesses processing, optimizing and adapting to massive amounts of data processing, and providing a range of possible answers to consider.
Quantum computing is still very niche, and the hardware and software required to handle the most complicated problems may not exist until after 2035.5 What is certain is that quantum computing has the potential to transform nearly every industry and deliver massive technological breakthroughs.
Data Centers Positioned for the Future
Disruptive innovations have far-reaching implications, and of course that includes the impact on data centers. Increased density will be a necessity, as will the ability to move data through networks at the speed required to realize the potential of each emerging or envisioned compute innovation.
CoreSite is well-positioned to enable each of these disruptive technologies – with the caveat that quantum computing poses exceptional challenges that are beyond reach right now. As one source observes: “Quantum computers are extremely sensitive and require vastly different cooling systems than today’s data centers provide.”6
However, our customers are executing high-density compute and leveraging near real-time data transport in artificial intelligence, blockchain and other use cases that are integral to digital transformation journeys and modernization. These technologies are the driving force that rapidly transform industries and markets alike. And for that, the world will never be the same.
Ready to discuss how disruptive technologies can help you reach a range of business objectives? Contact us about how we can support your ever-changing innovation needs.